Climate change and extreme weather are increasingly important for multiple stakeholders, including regulators, rating agencies, investors and risk managers. This briefing examines how climate change affects physical risks posed to insurers with South-East Asia exposure and the evolution of regulation associated with this risk.
Introduction
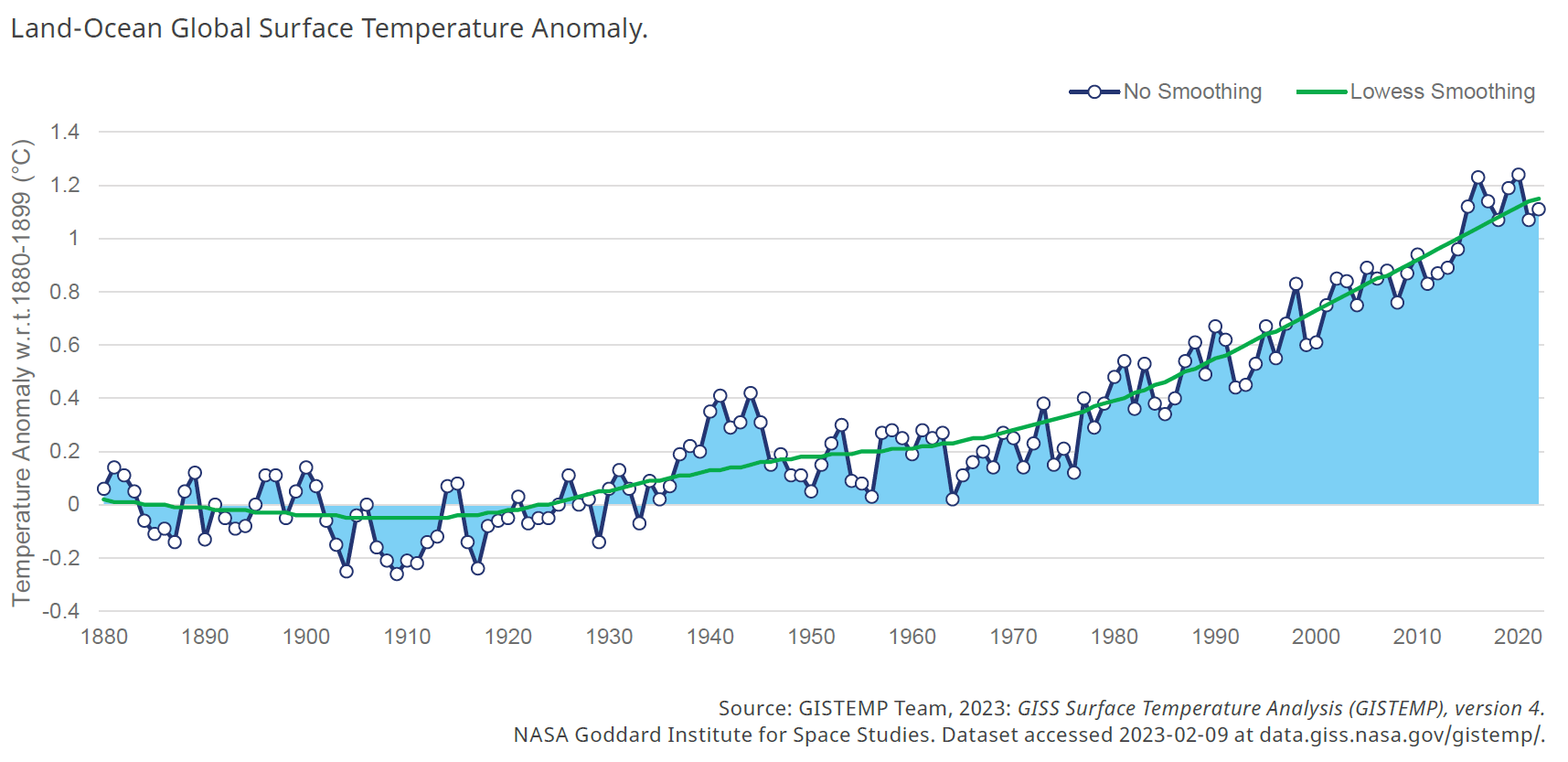
There is increasing pressure on insurers to understand climate change’s impacts on the damaging effects of weather. The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) reported that 2022 was the fifth-warmest year on record, with the average surface temperature 1.11°C warmer than during pre-industrial times (see figure below).
The global temperature is projected to increase further and will reach 1.5°C around 2030 without a radical reduction in emissions. These seemingly small increases in temperature can have a large non-linear impact on a wide range of perils, from drought to tropical cyclone storm surge. If there are no reductions in emissions in the medium term, then 3°C of warming is likely before the end of the century, which would bring more severe consequences.
Thailand’s 2011 floods were a devastating event, leaving more than 800 people dead and causing severe damage across northern and central regions of the country. There is increasing evidence that certain catastrophic events, such as these floods, are becoming increasingly likely to occur as a result of climate change. (Re)insurers can avoid unexpected losses—and help achieve long-term growth and profitability—by quantifying their exposure to the physical risk of climate change. (See figure below. Click the image to see larger version of the graph.)
Evolving Risk Landscape
The frequency and severity of natural catastrophes are expected to increase due to climate change. The subsequent impact on insured loss is highly dependent on the peril and region of interest, and is described in the section Climate Change Impact by Peril.
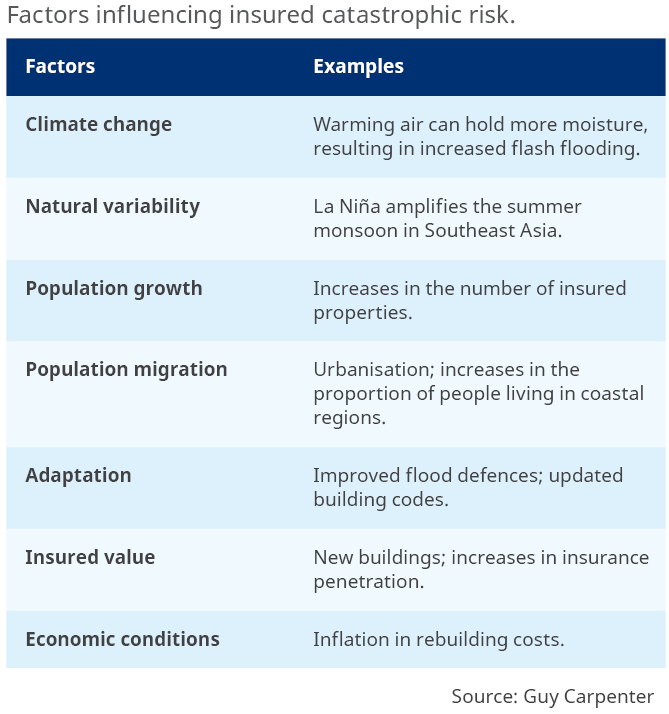
Climate change is not the only factor influencing how the financial catastrophic risk to re(insurers) changes from year to year. Climate change generally increases the risk gradually over time, although the financial impact may only be realised when a significant event occurs. In contrast, other factors can lead to more abrupt changes in risk, for example, inflation in rebuilding costs or the implementation of flood defences. These other factors will often have a larger impact than climate change, and we compare examples of them with climate change in the table below.
Managing Climate Change Physical Risk In South-East Asia
Regulation
Climate change presents 2 key forms of financial risk: those associated with a transition to a lower-carbon economy, and those related to the physical impacts of climate change. The physical impacts can be assessed and reported as either chronic or acute. Chronic physical risks are gradual changes in weather patterns, such as rising sea levels, droughts and extreme temperatures. Acute physical risks are sudden and severe events that can cause significant damage to property and infrastructure, such as hurricanes, floods, wildfires and storms. Mandatory reporting of these risks, often aligned with the recommendations of the Task Force on Climate-Related Financial Disclosures (TCFD), has come into effect in several jurisdictions.
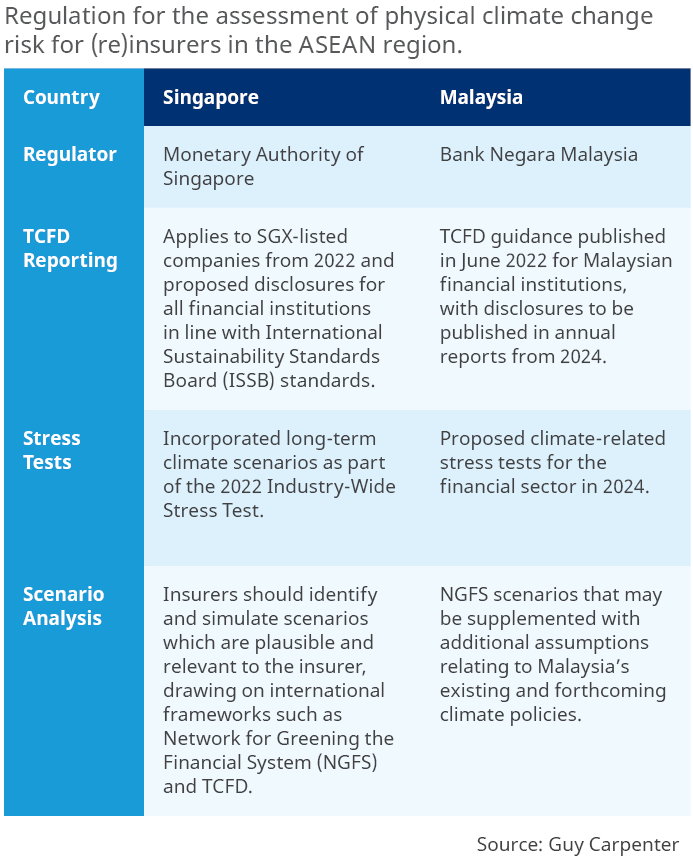
In the South-East Asia region, regulators are beginning to engage with the (re)insurance industry to build capacity and understanding of climate risks and their impact on financial stability. Given the complexity of these risks, responses are expected to be proportionate to the size, nature and complexity of the business. Scenario analysis has emerged as a key forward-looking tool to assess the potential impact of climate risks.
Supervisors in countries such as the Philippines and Thailand are proposing broader sustainability disclosures, particularly for listed companies. In Singapore and Malaysia, regulators have set out specific guidelines and requirements for climate change physical risk analysis. These are highlighted in the table below.
Climate Change Impact by Peril
We evaluate the impact of climate change on a peril based on observations, climate models and our understanding of the physical drivers. In cases where we have a consistent view—a long observational record, high-resolution climate model output and a good understanding of the physical drivers—then we will have high confidence in our assessment. Conversely, there are many reasons why we would have lower confidence, for example, if an observational record is short or unreliable or there is disagreement between different climate models. Here we summarise the climate change impact on tropical cyclones (TCs) and floods. Note that climate change does have a significant impact on a wide range of other perils, including wildfire, hail, drought and heat stress, but these typically have lower insured losses associated with them in South-East Asia.
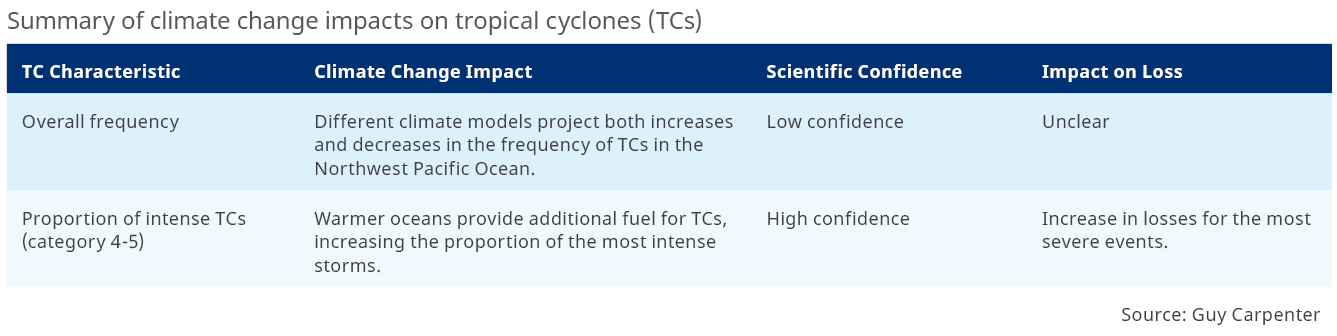
Climate Change Impacts on Tropical Cyclone
Climate change affects the frequency and severity of TCs in South-East Asia, as outlined in the table below. The impacts are wide-ranging, as the energy source of TCs (the ocean), the winds that inhibit their growth (wind shear) and the large-scale circulation pattern that steers them are all affected. There are also implications for the precipitation and coastal flooding associated with TCs, included in the table Summary of climate change impacts on flooding.
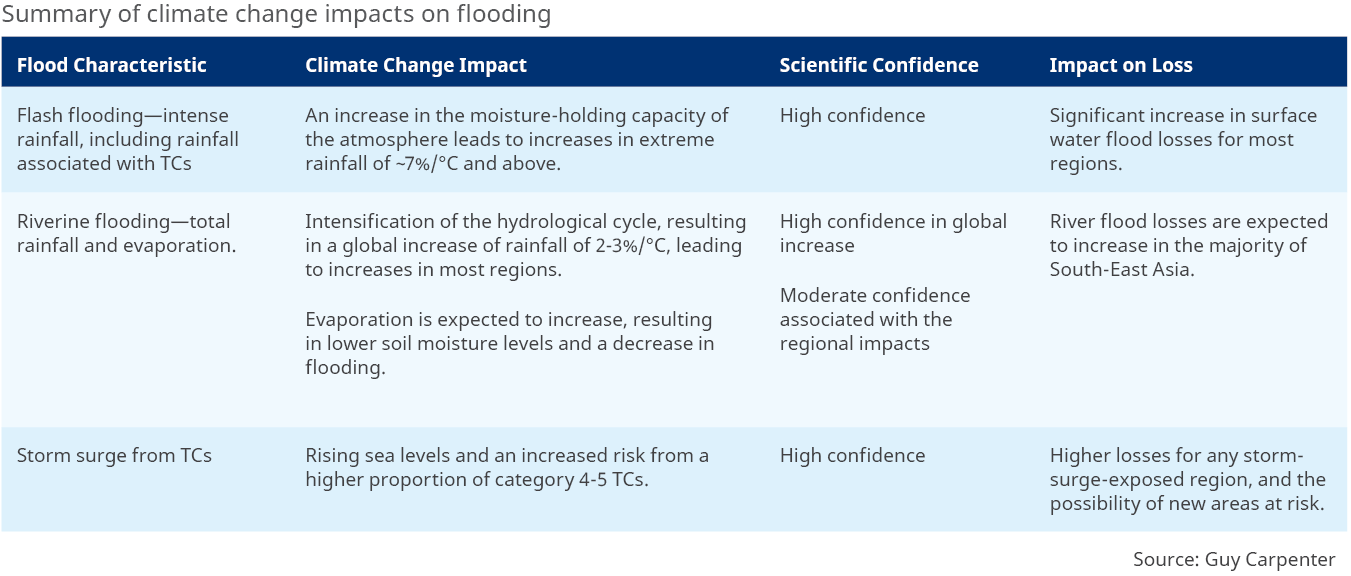
Climate Change Impacts on Flooding
The impact of climate change on flood is complex. Intense rainfall has a relatively direct link to surface water flooding, and therefore the climate change impact is generally well understood. In contrast, the response of river flooding to precipitation is dependent on a large number of factors, including soil moisture, temperature, snowmelt and catchment characteristics, and therefore changes are harder to predict and highly regional.
Quantifying your Climate Change Physical Risk
There are a growing number of reasons for quantifying your climate change risk:
- Responding to regulatory requests.
- Representation of risk to third parties, for example, credit rating agencies, investors or reinsurers.
- Making a TCFD-aligned climate disclosure.
- Incorporating climate change into risk management, pricing and capital decisions.
The type of risk assessment to carry out will be dependent on the use case. Important questions to consider before making any climate change assessment include the following:
- Is a qualitative or quantitative assessment required?
- What scenarios are of interest? This could be a specific emissions pathway and time horizon, for example RCP-8.5 in 2050, or instead a global warming level scenario, for example 1.5°C.
- Do you require an assessment of whether existing climate change is adequately represented in your current view of risk?
What form of data is required to embed the climate change assessment in your existing decision-making processes?
Guy Carpenter is helping our clients address these questions and quantify their climate change physical risk through a variety of methods. For the quantification of the risk, Guy Carpenter has developed proprietary tools, ranging from underwriting and accumulation layers to adjustments to third-party catastrophe models and in-house probabilistic models developed for climate change. Furthermore, we have a broad overview of market practices that can help clients benchmark their own activities.
For South-East Asia, we have an inland flood model adjustment that provides a fully probabilistic climate change assessment.
Conclusions
An improved scientific understanding of how perils are changing and an increasing number of regulators exploring climate related disclosures means quantifying your climate change risk has never been more important. Doing so may also help avoid unexpected loss from evolving tropical cyclones and flood risk. It is also important to be aware that climate change may not be the most significant driver of changes in loss for your portfolio. Other factors, such as natural variability and inflation, should be properly considered to inform risk management, pricing and capital decisions.